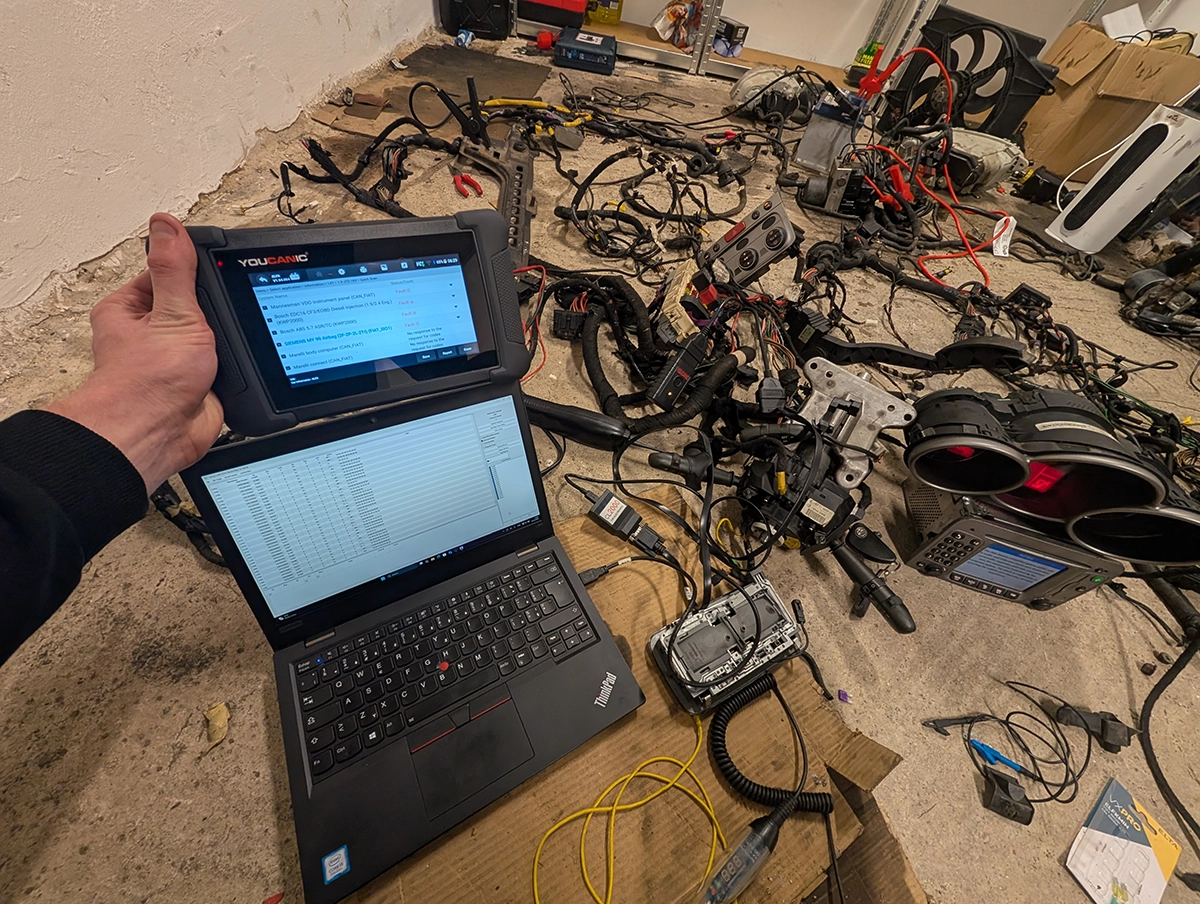
Most articles explain OBD2 in theory.
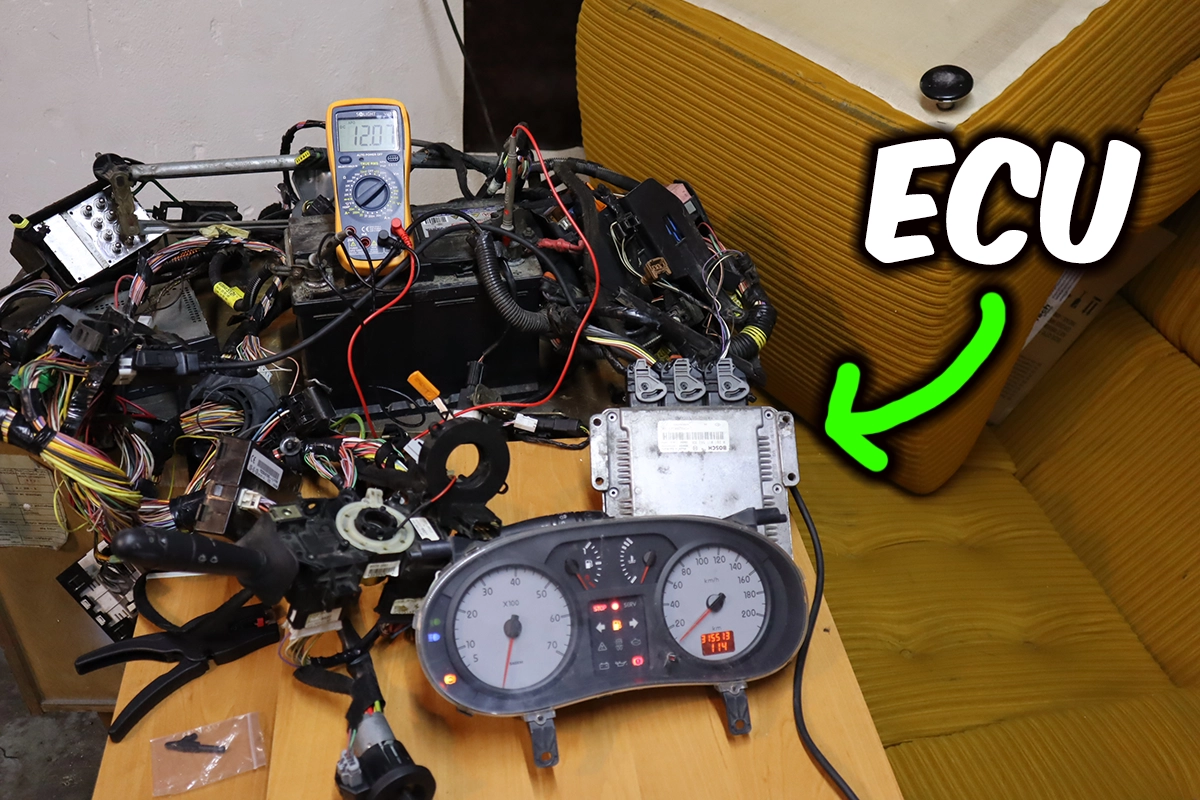
I’ll show you how it actually works using a real engine wiring harness I pulled out of a car and rebuilt on my desk.
This used to be a running car. Now it’s a full OBD2 system sitting on a bench. And that makes it much easier to understand what is really happening inside your vehicle.
Inside Your Car: It’s Not Just One Computer
Modern cars don’t have one brain. They have many.
The most important one is the engine control module (ECU). But that’s only one of many control units inside your vehicle.
In modern cars, you can easily have:
- Engine control module
- ABS module
- Airbag module
- Instrument cluster
- Body control module
- Radio
- Steering module
- Transmission module
Some modern vehicles have 50 to 70 control modules.
Each one controls its own part of the car.
How Control Modules Talk: CAN Bus
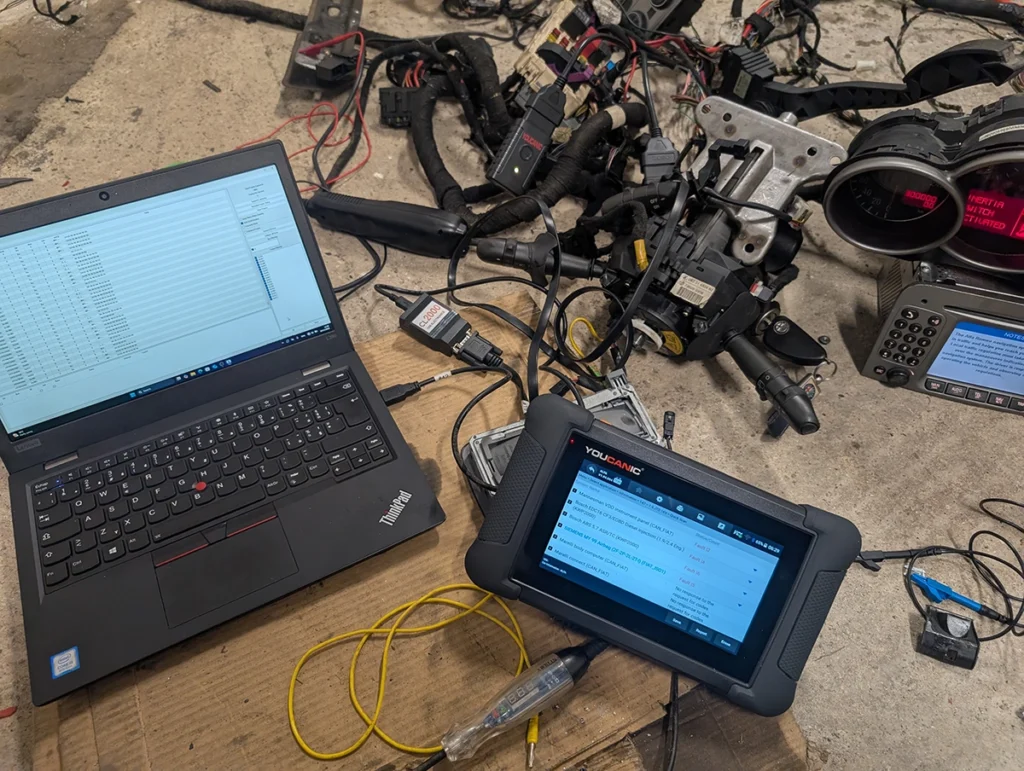

All these modules are connected together through something called CAN bus (Controller Area Network).
Physically, it’s just two wires:
- CAN High
- CAN Low
These two wires go into every control module. This is how modules share information.
When you turn the ignition on, thousands of messages start flying across these two wires. Every module constantly broadcasts and listens.
Your car is basically a network.
What OBD2 Really Is
Most people think OBD2 is the scanner.
It’s not.
OBD2 is the diagnostic software inside each control module.
Every module:
- Monitors its own sensors and components
- Compares values against factory limits
- Stores faults in its internal memory
For example, if fuel injectors are disconnected, the engine module detects incorrect electrical behavior and stores a fault code in its memory.
The diagnosing happens inside the control module, not inside the scanner.
Each module has:
- Its own processor
- Its own memory
- Its own stored fault codes
Where Fault Codes Are Stored
When something is wrong:
- The control module detects abnormal behavior.
- It sets a DTC (Diagnostic Trouble Code).
- The code is saved inside that module’s memory.
That memory stays there even if you disconnect the battery in many cases.
Modules also share some information with each other over CAN bus. That’s why we can later read these faults through the diagnostic port.
What the OBD2 Port Does
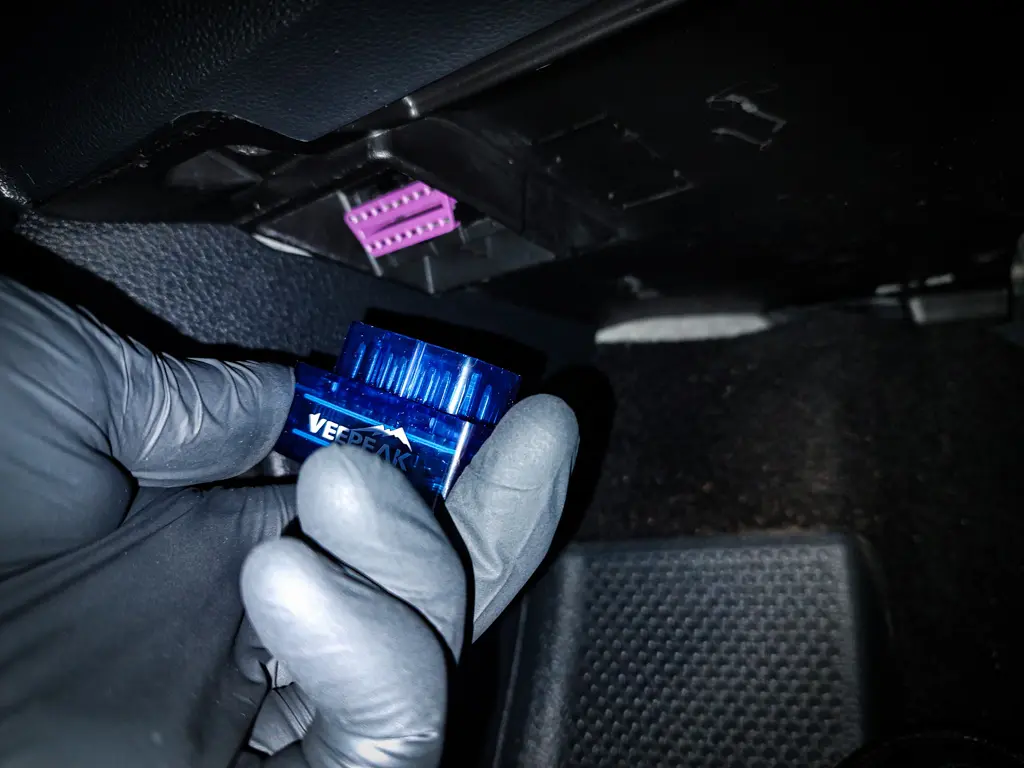

The OBD2 port is just an access point to the car’s communication network.
It does not diagnose anything.
It simply allows access to:
- Fault codes
- Live data
- Freeze frame data
- Readiness monitors
- Module coding
- Service functions
The scanner connects to this port and joins the communication network.
What a Scanner Actually Does
A scanner is a translator.
The car communicates in raw digital messages over CAN bus. If you log this traffic with professional tools, it looks like random hexadecimal data.
The scanner:
- Reads those messages
- Translates them into human-readable form
- Displays them as fault codes or live data
That’s it.
The scanner does not think, diagnose, or decide what’s broken.
It only translates what modules are already reporting.
Why Bidirectional Scanners Are Different
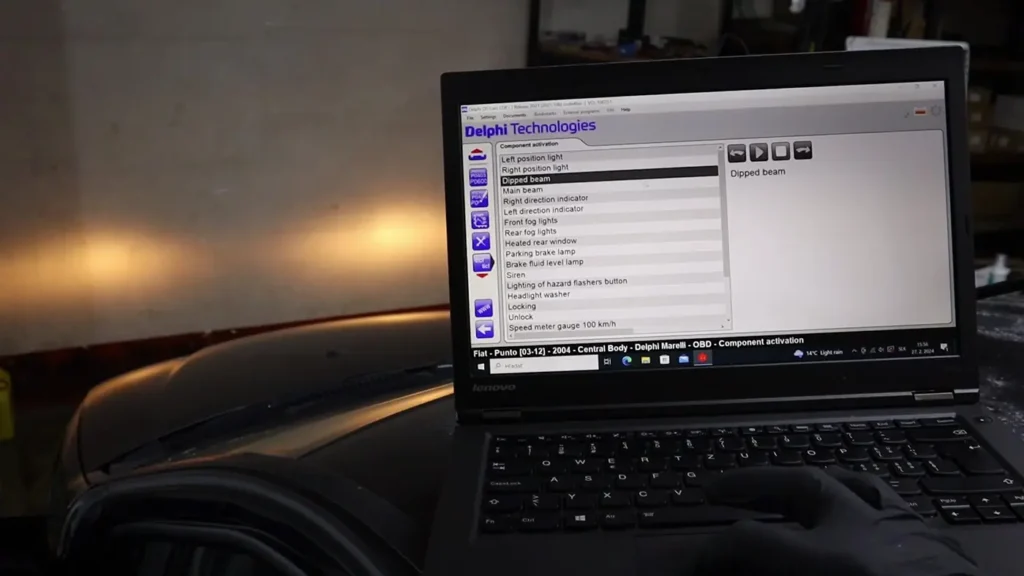
Basic scanners only read data.
Bidirectional scanners can also send commands.
For example:
- Activate engine fan
- Trigger fuel pump
- Cycle ABS pump
- Adjust instrument cluster settings
- Perform service resets
Technically, this is what happens:
- You press a function on the scanner.
- The scanner sends a command through the OBD2 port.
- The control module receives the request.
- The module performs the action.
Again, the scanner is just a middleman.
OBD1 vs OBD2
OBD started in the 1980s as manufacturer-specific systems.
OBD-I had:
- No standard connector
- Different protocols per brand
- Limited data
In 1996, the Environmental Protection Agency mandated standardized OBD-II for emissions compliance in the United States.
OBD-II introduced:
- A standard 16-pin connector
- Standard fault code format (P0xxx)
- Standard communication protocols
- Better emissions monitoring
Today, almost all cars worldwide use OBD-II or compatible systems.
How Many Modules Can You Read?
With a simple code reader, you usually access only the engine module.
With advanced diagnostic tools, you can access:
- ABS
- Airbag
- Body control
- Transmission
- Instrument cluster
- And many more
Modern cars can easily have 30 to 70 modules, and each one can store its own fault codes.
The Big Misunderstanding About OBD2
Most beginners think:
“The scanner shows a fault, so the scanner diagnosed the problem.”
Wrong.
The control module detected abnormal behavior. The scanner only showed it to you.
Real diagnosing means:
- Understanding live data
- Understanding system logic
- Knowing how sensors interact
- Testing components manually
That’s where real skill begins.
Summary: How OBD2 Works
- Sensors send data to control modules.
- Control modules evaluate that data.
- If something is out of range, a fault code is stored.
- The scanner connects through the OBD2 port.
- The scanner translates stored data into readable information.
- Advanced scanners can also send commands back to modules.
That’s the whole system.
It’s not magic. It’s software and communication working together inside your car.
Popular OBD2 guides
See all guidesBest OBD2 scanners in 2025
I constantly test new OBD-II scanners to give you the best options possible. Here is a full list of the best tools in all categories currently.


